The personal wiki of ...
From John Biggs ...
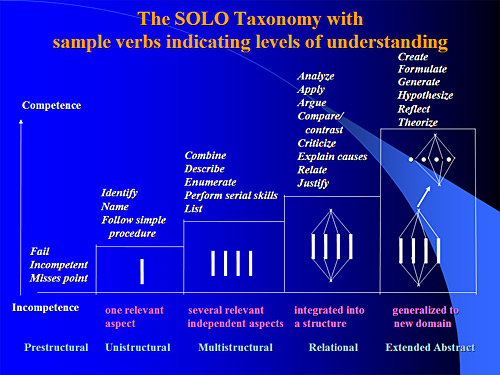 The Stages of Learning:
The diagram is divided into five distinct stages, each representing a different level of understanding:
The Stages of Learning:
The diagram is divided into five distinct stages, each representing a different level of understanding:
 The Stages of Learning:
The diagram is divided into five distinct stages, each representing a different level of understanding:
The Stages of Learning:
The diagram is divided into five distinct stages, each representing a different level of understanding: -
Prestructural (Incompetence):
- Description: The learner is incompetent and misses the point. They don't grasp the basic concepts.
- Visual Representation: A simple vertical line (|).
- Example: A student asked about photosynthesis might have no idea what it is or what it involves.
-
Unistructural (One Relevant Aspect):
- Description: The learner can identify one relevant aspect of the topic. They have a basic, superficial understanding.
- Visual Representation: Three vertical lines (|||).
- Example: The student might know that plants need sunlight for photosynthesis but not understand how or why.
-
Multistructural (Several Relevant Independent Aspects):
- Description: The learner can identify several relevant aspects but treats them independently. They haven't made connections between them.
- Visual Representation: A diamond shape with lines inside.
- Example: The student might know that plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis but not understand how these elements interact.
-
Relational (Integrated into a Structure):
- Description: The learner can integrate the different aspects into a coherent structure. They understand the relationships between the parts.
- Visual Representation: Two interconnected diamonds with lines inside and an arrow pointing to the next stage.
- Example: The student understands how sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide are used in photosynthesis to produce glucose and oxygen.
-
Extended Abstract (Generalized to New Domain):
- Description: The learner can generalize their understanding to new situations and apply their knowledge in different contexts. They can think abstractly about the topic.
- Visual Representation: Two interconnected diamonds with lines inside and an arrow pointing to the next stage.
- Example: The student can explain how photosynthesis is related to other biological processes like cellular respiration and how it impacts the global ecosystem.
- Prestructural: (None listed)
- Unistructural: Identify, Name, Follow simple procedure, List.
- Multistructural: Combine, Describe, Enumerate, Perform serial skills, List.
- Relational: Analyze, Apply, Argue, Compare/contrast, Criticize, Explain causes, Relate, Justify.
- Extended Abstract: Create, Formulate, Generate, Hypothesize, Reflect, Theorize.
 Users/Ian
Users/Ian
