

Speaker: Ruibin Bai, University of Nottingham Ningbo China
Date: 12 May 2025
Time: 4:00 - 5:00pm (Beijing Time, UTC+8)

Ruibin Bai is a professor and Head of the Artificial Intelligence and Optimisation (AIOP) group at the University of Nottingham Ningbo China. He also leads Ningbo Digital Port Technologies Key Lab. His main research interests include computational intelligence, reinforcement learning, digital twin, operations research, scheduling and optimisation with a special focus on transportation systems and port logistics. He has published over 140 academic papers and currently serves as Associate Editor for European Journal of Operations Research and Networks. His work is recognized in industry through “Huawei Spark Award” in 2022. Under his leadership, his team has developed algorithms and software systems that have been commercialized in Ningbo Port and PingAn Good Doctor.
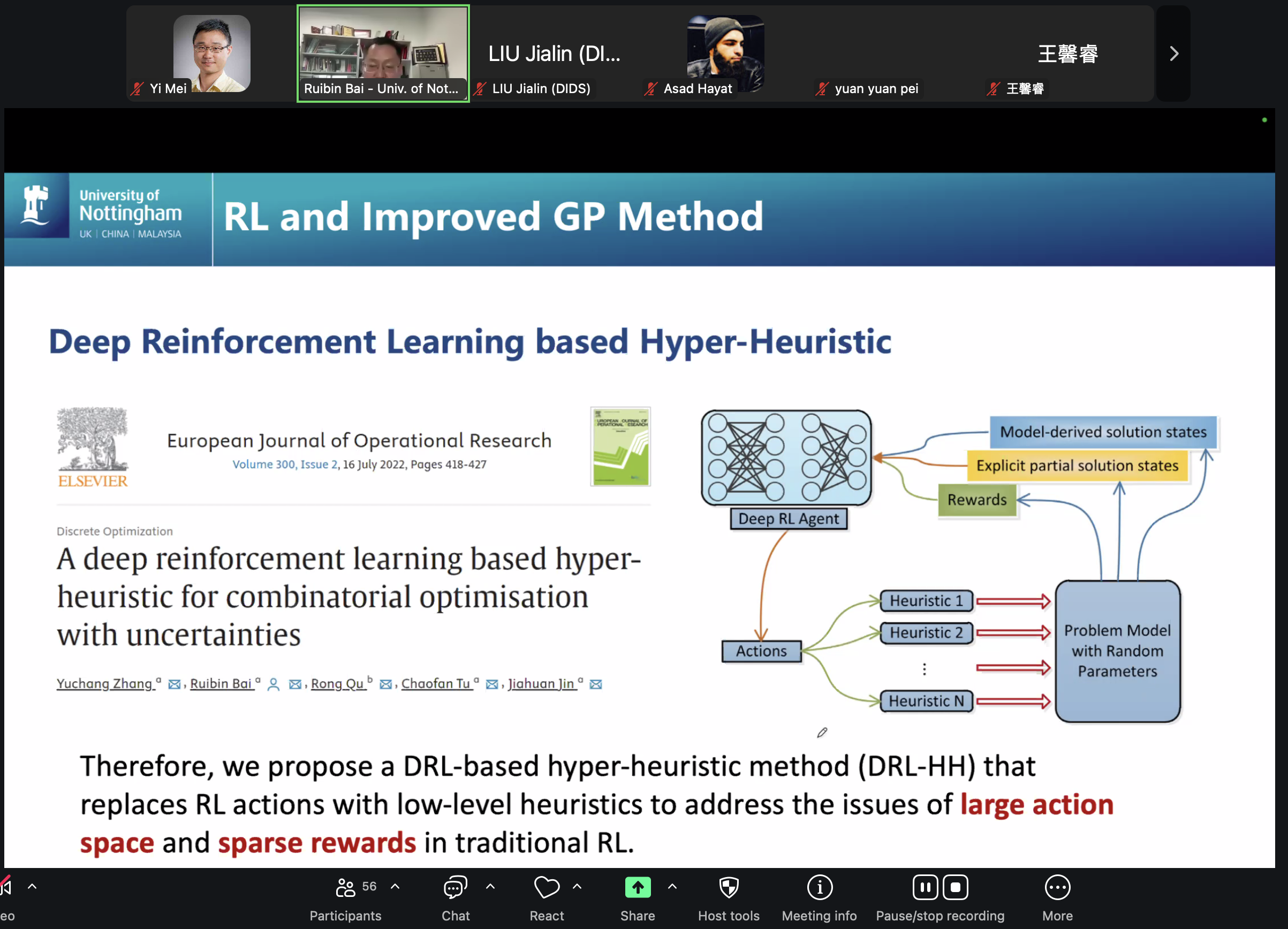
Many real-life optimisation problems are intended for complex systems with limited predictability. Such systems are characterized by the large scale of the problem sizes, nonlinearity, multi-objectivity and uncertainties. In marine container terminals, truck dispatching optimization is often considered as the primary focus as it provides crucial synergy between the sea-side operations and yard-side activities and hence can greatly affect the terminal throughput and quay crane utilization. However, many existing studies rely on strong assumptions that often overlook the uncertainties and dynamics innate to real-life applications. In this talk, we investigated several learning based dynamic algorithms for transportation. Different from offline methods that search for full solutions directly, the proposed generative methods focus on obtaining a generative policy (heuristic) that makes more balanced decisions between two extremes: near-term greediness and long-term reward forecasts which are mostly over-optimistic under uncertainties. This presentation shall report a deep reinforcement learning hyper-heuristic and a genetic programming ensemble hyper-heuristic method. Experiment studies show our proposed methods have good generalization and achieve the state-of-the-art results on the problems derived from real-life transportation problems.
The Webinar went very successful, with 50+ participants.
The video recording of the Webinar can be found here.
The slides of the Webinar can be found here.
Back to the Webinar Series